Introduction to Statistical Inference
현재 정리하는 내용은 KAIST EE의 이융 교수님, Probability and Intorductory Random Process 강의를 참고하여 작성했습니다.
What is Statistical Inference?
- 몇 개의 예제를 통해 Inference가 무엇을 의미하는지 확인해보자.
- Take 1000 voters uniformly at random, and count the popularity of each candidate to infer the true popularity.
→ What is true popularity? - COVID-19 has spread over a collection of people, and we collect a sample of COVID-19 infectees to infer the true source of infection.
→ What is true source of infection? - When an original signal S is transmitted over the School Wi-Fi connection, the received signal X becomes X = aS+W, where 0 < a < 1 and W ~ N(0, 1). If we have 10 samples of (S, X) values, what is the inferred value of a?
→ What is value of a?
- Take 1000 voters uniformly at random, and count the popularity of each candidate to infer the true popularity.
- 위 3가지 예제를 통해 Inference는 정보를 추출해내는 Process라는 것을 알 수 있고, 이 때 unknown variable or an unknown model을 기반으로 한다는 것을 알 수 있다.
Statistical Inference : Three Main Ideas.
- 앞서 말한 내용에서 주된 3가지의 아이디어를 생각해보자.
- Samples are likely to be a good representation of the unknown.
- There exists uncertainty (i.e, noise) as to how well the sample represents the unknown.
- How to obtain samples has impact on inference
Inference, Real World, Probability Theory
- 이 세 가지의 연관성을 알아보자.
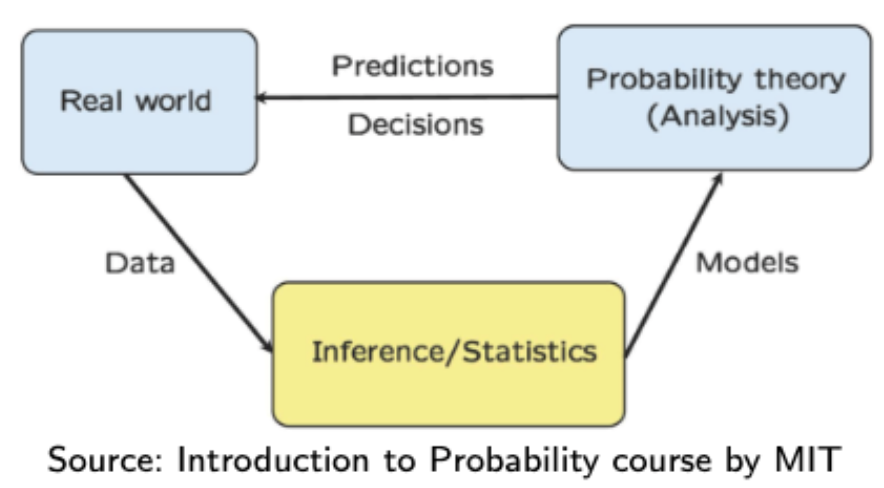
→ 그림에서 나온 것과 같이 세 가지는 모두 연관이 되어있다. - Inference
→ 현실 세계의 데이터를 갖고, probabilistic model 또는 parameters를 결정하는 것
What to infer? Unknown Model vs. Unknown Variable
-
이 둘의 차이가 무엇일까? 앞서 예제에서 봤던 것 중 하나를 가져와보자.
→ When an original signal S is transmitted over the School Wi-Fi connection, the received signal X becomes X = aS+W, where 0 < a < 1 and W ~ N(0, 1). If we have 10 samples of (S, X) values, what is the inferred value of a?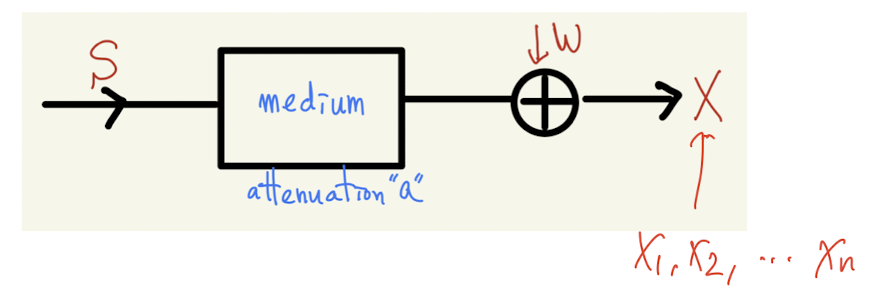
→ X = aS + WModel Building Variable Estimation Know the original signal S
Observe X
Infer the model parameter aKnow the original signal S
Observe X
Infer the original signal S -
이 둘의 다른 점은 있지만, 즉 다른 질문을 던지지만 동일한 수학적 구조를 갖게 된다.
What kind of inference? Hypothesis Testing vs. Estimation
| Hypothesis Testing | Estimation |
|---|---|
| Unknown : a few possible ones. → Finite discrete Goal : small probability of incorrect decision → How can we evaluate my decision? Ex. Something detected on the radar. Is it a bird or something? |
Unknown : a value included an infinite, typically continuous Goal : Finding the value close to the true value. Ex. Biased coin with unknown prob. of head. What is data of heads Note. If u have the candidate values of {1/4, 1/2, 3/4}, then it’s a hypothesis testing problem. |
Different views: Bayesian vs. Classical
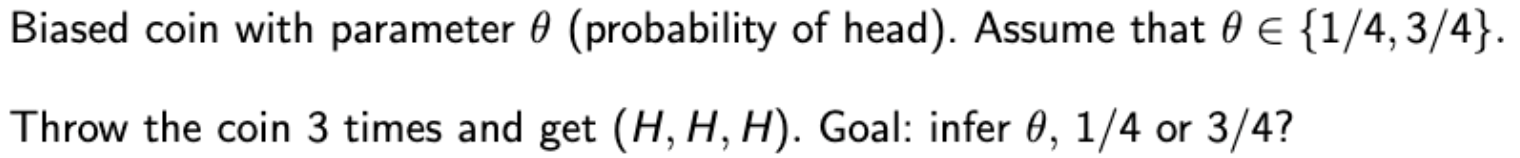
→ Infere할 것이 {1/4, 3/4}이므로, Hypothesis testing.
→ 직관적으로 생각해본다면, HHH가 나왔으니까 3/4일 확률이 더 높다. 이걸 Bayesian 관점과 classical 관점으로 확인해보자.
| Bayesian View | Classical View |
|---|---|
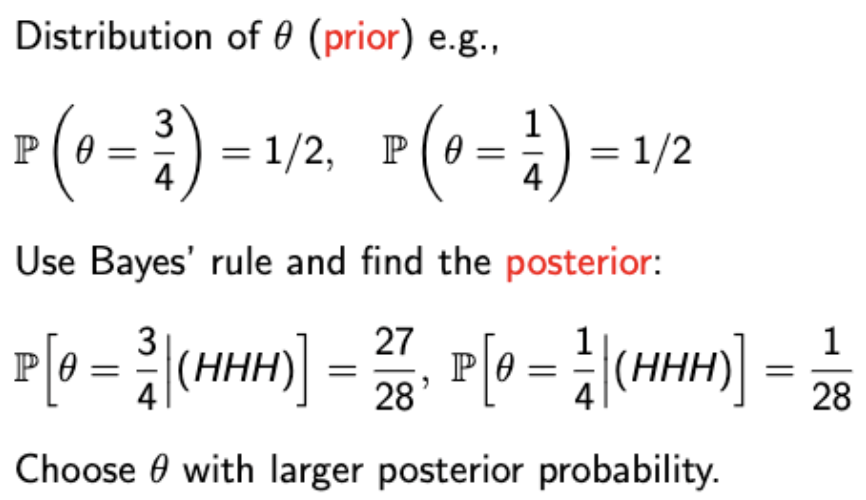 → Prior distribution을 통해 posterior를 계산하는 전형적인 Bayesian 방법이다. → 가장 큰 θ를 고르는 방식은 MAP라고 한다. 후에 나온다. |
 → 옆에 있는 Bayesian과 다르다는게 느껴진다. → θ가 있다는 가정 하에 HHH일 확률을 구하는 방식으로 한다. |
-
이거는 Bayesian rule 계산 방식

-
수식으로 확인해보았으니 이제 글로 확인해보자.
Bayesian View Classical View Unknown : RV with some distribution (prior)
Observe : Data X, posterior distribution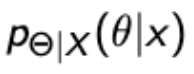
→ 표본으로부터 제공된 정보와 함께
unknown parameter의 확률 분포에 대한 지식을 사용하여 추론
Unknown : Deterministic value
Observe : Data X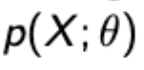
- 그럼 누가 더 좋은 방식이야?
→ 이것에 대한 정답은 아직 없다. 아래 예제를 한 번 확인해보자. - Example. mass of the electron by noisy measurement.
Classical View : unknown이기는 한데,,,전자의 질량은 당연히 상수지. 그러니까 모델링할 수 있는 RV는 없어.
Bayesian : 아니! 우리는 some range of candidate values를 이전 측정에서 구할 수 있으니까 당연히 가능해! - 이렇게 서로 다른 주장을 할 수 있다. 따라서 누가 더 좋고 말고 할 것이 없다.
- 근데, Bayesian은 다차원 데이터에 대한 계산의 용이성이 있다는 점은 존재한다.
→ MNIST는 28 by 28의 다차원 데이터이다.